Details of belt conveyor parts are given below:
- Conveyor belt
- Drive unit
- Electric Motor
- V belt
- Output coupling
- Gear box
- Input coupling
- Pulleys
- Head pulley
- Tail pulley
- Snub pulley
- Take up pulley
- Bend pulley.
- Idler
- Guide idler
- Carrier idler
- Return idler
- Impact carrying idler
- Structure or stringer
- Skirt board
- Belt cleaner or scrapper.
- Conveyor hood or roof.
- Conveyor walk way
- Back stop
- Diversion drum
- Idle drum
- Loading chute
- Rubber roller
- Self-aligning carrying idler.
- Deck plate
- Zero speed switch
- Beltsway switch
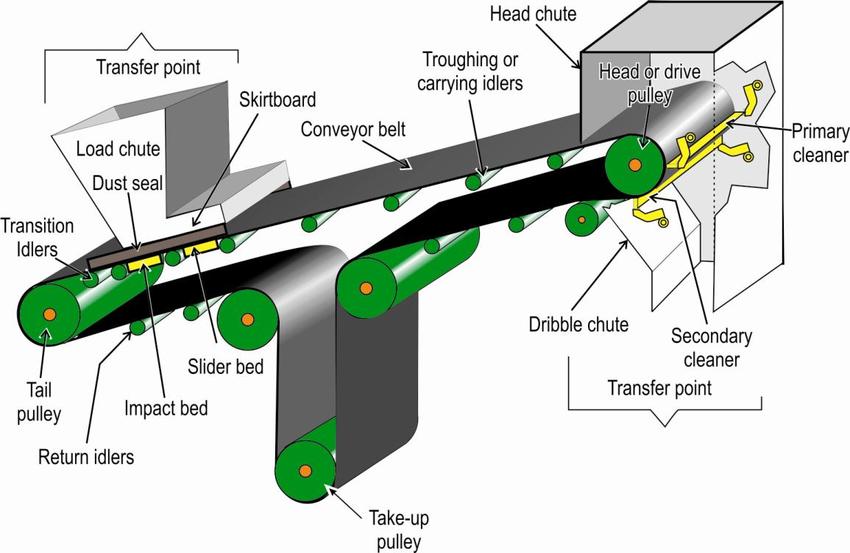
Table of Contents
Pulleys:
The pulleys are mechanical equipment that supports the conveyor belt and also moves the belt, controls its tension, and tracks the conveyor belt. There are different types of pulleys are used in conveyor systems.
- Head pulley
- Tail pulley
- Snub pulley
- Take up pulley
- Bend pulley, etc.
Head pulley:
Head pulley connected with gearbox and gearbox connected with motor. Normally the discharge end of the conveyor where the material is transferred to another conveyor is called the head end and the pulley in this end is called as head pulley. Head pulley is designed as stronger and bigger as compared with other pulleys. Lagging is provided in the head pulley its main function is to increase the grip of the rubber belt over-head pulley.
Tail pulley:
The pulley which is situated in the receiving end of the conveyor is called a tail pulley. Sometimes, screw take-up will be situated in the tail pulley. This pulley is moveable when take-up is kept in this. Actually, this acts as a support when the belt takes a turn.
Snub pulley:
The snub pulley is incorporated into the design of a conveyor in order to increase the angle of wrap of the belt on a drive pulley. The greater wrap angle on the pulley allows more power to be introduced into the belt as it passes around the drive pulley without any slip. In this way, power drivers are needed on longer conveyors or conveyors with high conveying loads.
Take-up pulley:
The main function of taking up a pulley is to provide an emergency reserve belt, and also its other main function is to maintain belt tension for conveyor belts having a small length take-up pulley is not required.
Electric motor:
The electric motor is connected to the input shaft of the gearbox by coupling is called input coupling and the output shaft of the gearbox is connected to the head pulley of the conveyor by the coupling which is called output coupling.
Idlers:
Conveyor belts are operated through idlers. The need for idlers is to give proper support to the conveyor and also to the material to conveyor. An endless conveyor belt in a conveyor structure is dragged from the tail pulley where the material is loaded on the conveyor, to the head pulley or drive pulley where the material is discharged between a conveyor tail and head pulleys, where the distance is a number of kilometers or merely a few meters, the carrying and return stand belting is idlers sets. The rolls are fitted with antifriction bearings with seals and with inadequate lubrication packed into them. The friction between the roller surface and the belt makes the roller rotate and thus material is transferred from one point to another, through the belt conveyor. Without frame is called a roller and the with frame is called the idler.
The jammed or damaged idlers should be replaced immediately. Because they have the high potential to damage the belt. (Specially belt joints).
Guide idler:
The main function of the guide idler is it does not allow the conveyor belt to go out of frame. So that guide idler helps to prevent damage of conveyor belt.
Return idler:
It is used at the lower end of the conveyor belt. It supports the lower portion of the conveyor belt. You can find it in 1.5 meters to 2-meter distance in the conveyor system.
Impact carrying idler:
Impact idlers outer side has a rubber coating. The main function of an impact-carrying idler is to prevent shocks and avoid impacts on a conveyor belt while material transferring or where material falls over the conveyor belt.
Self-aligning idler:
It aligns the lower portion of the conveyor belt.
Spiral return idler:
The main function of the spiral return idler is it generates friction.
Garland idler:
The garland idler’s function is the same as compared to carrying idler. Garland idler supports the belt’s upper part like carrying idler. Actually, it bears the conveyor belt’s load. In this idler, all idlers are connected to each other.
There is one drawback if one idler is damaged and it does not work then the whole frame will require replacement.
Structure or Stringer:
The structure supports and maintains the alignments of the idlers and pulleys.
Skirt Board:
A Skirt board is generally provided at the loading point in the belt and retains the material on the belt until it reaches the belt speed. Also, to control the unloading turbulence the skirt boards are necessary. Skirt boards are provided to avoid spillage during receiving the material from the previous belt.
Belt cleaner or scrapper:
The main function of the conveyor belt is to carry material and during this process, the material sticks to the belt for which belt scrappers are used to clean the belt.
- It avoids the material build up in snub pulley and return idler.
There are three types of scrappers:
- Primary scrapper
- Secondary scrapper
- V-plough scrapper
Conveyor hood or roof:
- It is used to protect the belt material from climate change condition like rain.
- It is made up of Galvanized sheet material.
Conveyor walkway:
- Generally, it is provided for maintenance purpose of conveyor belt.
Backstop:
It is used in inclined belt conveyors to prevent belt conveyor movement in the reverse direction.
Take-up:
It is necessary to maintain tensions at the point to prevent slippage on the drive pulley.
Types of take-up:
There are two types of take-ups.
- Manual or screw type
- Vertical gravity take-up or Horizontal gravity take up
- Manual or screw type:
The screw-type or manual type provides enough movement to establish initial tension in the belt and to provide periodic readjustment as the belt stretches. Generally, it is employed to a tail pulley for giving tension to the belt. It is generally applied to the conveyor belt of having a length less than 50 meters.
- Vertical gravity take-up or Horizontal gravity take up (HGTU or VGTU):
Horizontal or vertical take-ups provide sufficient travel to handle any elastic change due to load variation.
Chutes:
Chutes are generally of two types:
- Feed chute
- Discharge chute.
Feed chutes are used for feeding the materials in the belt and it is situated near the tail pulley and the discharge chute is used for discharging the materials and is situated near the head pulley.
Once the rate of feed is determined and set, the speed and placement of material on the belt are controlled by the loading chute and skirt board. The chute width must be greater enough to accept material lying of extreme edges of the preceding belt usually has substantial velocity, there is a choice of positions for the receiving end of the chute. It can be placed in such a way to reduce the impact on the chute and less material degradation. During starting and stopping when the load has a trajectory too low to reach the chute. Provision for convergence and dribble chutes are also available.
Deck plate:
- Deck plate must be given below the troughing belt.
- Deck plate protect the entrapment of spillage material between the rotating pulleys and the belt.
- The locations where the conveyor gallery is passing over the road or working area. The deck plate below the return plate must be provided.
- For repairing or fixing of a deck plate, the gas cutting or welding safety standards should be followed.
Zero speed switch (ZSS)
- Zero speed switches also known as speed activity sensing switches are used to detect whether a rotating shaft is turning in various machines conveyors, powerplant, sugar, textile, paper, etc.
- Control actions are:-
- Zero speed protection
- Under speed protection
- Over-speed protection can be achieved.
The Zero speed switch (ZSS) switch should be cleaned thoroughly at a regular interval.
Belt sway switch (BSS):
A belt is considered to be aligned properly, when under full load or in no-load the edges of the running belt consistently remain within the width of the pulley faces and within the confines of other rolling components, such as idlers. If the running belt deviates from the above definition of aligned tracking, it is called ‘belt sway’. The length of the lever of the belt sway switch should be in the range of the belt during belt sway.
Pull cord Switch:
Pull cord switch also known as rope operated emergency switch is used as a safety switch to stop the conveyor belt in case of an emergency. The pull cord switch with an LED indicator should be used.
NOTE:
- Do the positive isolation of all the electrical power sources of conveyor system before maintenance.
- Never stop the in loaded condition. Stop the conveyor belt, when it is empty.
