A circuit breaker is a piece of equipment or a switching device that can make or break a circuit either manually or automatically under normal or faulty conditions. A circuit breaker is a safety device used to prevent damage to electrical circuits or electrical appliances on overload or short circuit conditions. The characteristic of the circuit breaker has made it very useful equipment for switching and protection of various parts of the power system.
Circuit breaker plays an important role in safeguarding the circuit and the appliances and also our home from any mishaps due to overload or short-circuit condition. Voltage fluctuation is common in most countries so that circuit breakers help to prevent damage to appliances.
The circuit breaker is one of the most vital safety mechanisms in our houses. Circuit breakers are installed in an electrical panel and each circuit is attached to a singular breaker. In the circuit, breaker reset is possible after the trip.
Table of Contents
Purpose of a circuit breaker:
In the simplest term, the circuit breaker interrupts or stop the abnormal flow of electric current and save the electrical system from damage. Basically, it is designed to open or close the electric circuit and the circuit breaker is the most important safety mechanism in our home.
Actually, when the device on the circuit draws more current than the circuit is designed for then the circuit breaker opens the circuit and stops the flow of electric current, and prevents the appliances or circuit from damage. Circuit breakers and fuses work on the same principle i.e., de-energizing the circuits allowing them to work easily and prevent faults.
Types of Circuit Breaker:
According to different criteria, there are different types of circuit breakers. According to their arc quenching media, the circuit breaker can be categorized as:
- Oil circuit breaker.
- Air circuit breaker.
- Sulphur hexafluriide (SF6 ) circuit breaker.
- Vacuum circuit breaker.
According to their services the circuit breaker can be categorized as:
- Outdoor circuit breaker.
- Indoor breaker.
According to the operating mechanism of circuit breakers they can be categorized as:
- Spring operated circuit breaker.
- Pneumatic circuit breaker.
- Hydraulic circuit breaker.
According to the voltage level of installation types of the circuit breaker are referred to as-
- High voltage circuit breaker.
- Medium voltage circuit breaker.
- Low voltage circuit breaker.
High voltage circuit breaker:
- During the normal operation of power system, the circuit breaker provides isolation between circuits and power supplies.
- The most basic function of a circuit breaker is to interrupt the circuit during short circuit and overload conditions.
- The function of a circuit breaker is to open its contacts with in a predetermined time period as fast as possible to limit the amount of energy diverted in to any unnecessary path.
- The circuit breaker has to handle different types of currents such as the resistive load current, inductive short circuit current and capacitive current in unloaded lines.
- The circuit breaker has to close under faulty conditions during which severe arc with peak instantaneous fault current appears across the contacts before the physical touch.
Examples of high voltage circuit breakers are: Arc break circuit breaker, Oil circuit breaker and vacuum circuit breaker, etc.
Low voltage circuit breaker:
- A circuit breaker is a connecting device that closes and breaks an electric circuit up to its ultimate breaking capacity.
- Although its main function is to break the short circuit and over loaded currents by self-energized action. It also breaks normal currents and overload currents by voluntary action from external sources.
- After opening it provide voltage insulation to the broken circuit.
- Examples of low voltage circuit breakers are: Switches, fuses and MCB’S, etc.
Advantages of Circuit breaker:
- Easily reusability (Easily reset)
- No isolation.
- All poles are operated at the same time.
- Used as ground fault detection (ELCB).
- Indication of trip.
- Auxiliary contact available.
- Used as on/off switch.
- Characteristic curve remains unchanged.
Dis advantages of Circuit breaker:
- It is high cost and complex.
- Operating speed low.
- Require maintenance for mechanical operation, etc.
What is a fuse?
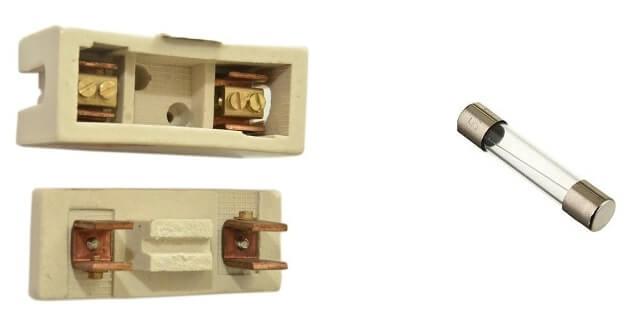
Fuse is a short piece of metal, inserted in the electrical circuit, which melts when excessive current flows through it and thus breaks the circuit. The fuse element is generally made of a material having a low melting point, high conductivity, and least deterioration due to oxidation (i.e., silver, copper, etc.) and the fuse is inserted in series with the circuit.
- It carries normal load current continuously without generating excessive temperature.
- When the magnitude of current exceeds the level that results in the melting of fuse material due to temperature effect, the circuit breaks and disconnects from the mains.
- Fuse is a complete device that consist of a fuse casing (base) and a fuse link where the fuse link is connected to the terminals.
Characteristics of fuse:
- High conductivity.
- Free from deterioration due to oxidation.
- Low cost, etc.
- Thermal characteristics.
- Very inverse melting characteristics.
- Interrupting characteristics.
Advantage of fuse:
- Low cost and simple.
- Operating speed is very high.
- No maintenance is required (Because there is no mechanical part in fuse).
Disadvantages of fuse:
- Slow in operation.
- Power loss due to heat.
- Fuses do not respond to high voltages it only cares about current flowing and is not likely to melt and save the house in case of a direct lightning strike.
- Do not give protection against voltage surges.
- They need to be replaced every time.
FAQs for Circuit Breaker:
Why circuit breaker is better than a fuse?
Firstly, when a fuse blows out, it takes quite some time to replace it and restore the power supply. Secondly, a fuse cannot successfully interrupt heavy fault currents that result from faults on modern high voltage and large capacity circuits. Due to this disadvantage, the use of fuse is limited to low voltage and small capacity circuits where frequent operations are not expected (i.e., for lighting circuits and branch circuits). Where a circuit breaker is much faster and reliable than a fuse.
What is overload?
Overload is excess amperage flowing over a circuit.
What is a short circuit?
An unexpected electrical flow, that travels from sources that are electrically conductive.
Example: –
1. Wire being stripped and touched by a tree limb.
2. Two wires with different voltages touching together.
Why circuit breaker trips?
1. Due to overload circuit.
2. Due to short circuit.
3. Due to ground fault.
Related topics:

