Table of Contents
What is confined space?
Confined space is a space that meets all the criteria:
- Large enough to bodily enter and work.
- Limited entry and exit.
- It is not designed for continuous human occupancy.
- Has unfavorable natural ventilation due to stagnant air, no free air movement, oxygen deficiency or enrichment or nitrogen atmosphere.
- Has contaminated air with toxic or/and flammable gas, dust, etc and
- May cause engulfment (swallowing) in unstable or loose material.
Boiler, degreaser, pumping station, mills, septic tank, Barges, utility vault, trenches, etc are considered as confined space.
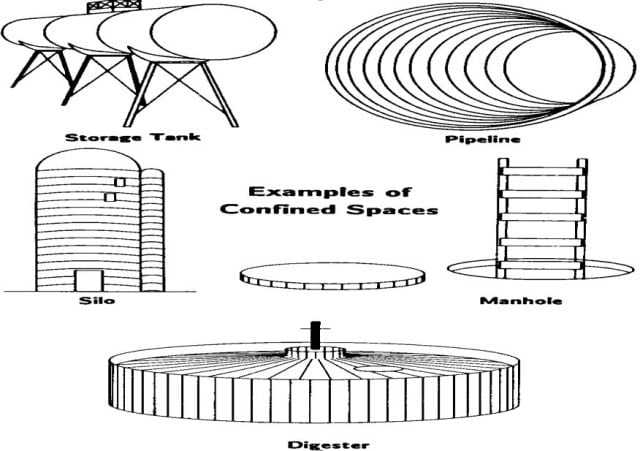
Types or example of Confined Spaces:
- Storage tank
- Process vessels / Reaction Vessel
- Pressure Vessels
- Boilers
- Tank cars (trucks)
- Tank wagons
- Digester
- Wells / bores
- Sumps
- Pits
- Silos
- Pipes
- Ducts
- Gutters
- Tunnels
- Sewers
- Vats
- Bilges
- Shafts
- Manhole
- Furnace
- Pipeline.
Categories of confined space:
| Severity | Class | Nature of hazard | Clearance giving authority | Example of confined space |
| High | A | Gaseous | CIF certified competent person | Gasholders, Drainage manholes, boilers, ESPs |
| Medium | B | Entrapment | CIF certified competent person | Bins, Hoppers, Dust catcher, Cyclones |
| Low | C | Others | The departmental trained competent person with safety professionals | Cable tunnel, conveyor tunnels |
Hazards of Confined Spaces :
- Oxygen Deficient Atmospheres.
- Oxygen Enriched Atmospheres.
- Flammable Atmospheres.
- Toxic Atmospheres.
- Poor lighting and ventilation.
- Unexpected activation of machinery
- No way or no time available for the exit.
- Nonspecific work practices.
- Temperature Extremes.
- Engulfment Hazards.
- Noise, Slick/Wet Surfaces, Falling Objects.
- No way or no time available for the exit.
- Engulfment (burying) in loose material.
Many workers are injured and killed each year while working in confined spaces. A confined space can be more hazardous than others.
Other hazards are suffocation, burning, poisoning, explosion, drowning, freezing, crashing, entrapment, scalding, stroke, heat stress, radiation, physical trauma, injury by moving machinery, slipping or falling, etc.
Many fatal and serious accidents have occurred while working in a confined space. Three reasons flammable air mixture, toxic gases, and oxygen deficiency – are found responsible for such accidents. Tanks (vessels) with top cover open but all other sides closed, should be considered as a confined space, because, in such a situation, persons working inside have to face direct fire, explosion, or toxic exposure and have no other way to run away except the only way of their entry. Therefore doubtlessly and as per the above statutory definition, such a situation/condition is a confined space. One worker died due to solvent fire, one died due to chloroform vapor and two died due to nitrogen (oxygen deficiency) atmosphere in such confined spaces.
Oxygen Deficient Atmospheres :
Normal air contains 21% Oxygen (O2). An O2 level of 19.5% or less is considered O2 deficient. A reduction in O2 can be caused by rusting, decomposition, or replacement by another gas like nitrogen or carbon dioxide. lack of O2 can cause a person to collapse and die.
| 19.5 % | Minimum acceptable oxygen level. |
| 15 – 19% | Decreased ability to work strenuously. Impair coordination. Early symptoms. |
| 12-14% | Respiration increases. Poor judgment. |
| 10-12% | Respiration increases. Lips blue. |
| 8-10% | Mental failure. Fainting. Nausea. Unconsciousness. Vomiting. |
| 6-8% | 8 minutes – fatal, 6 minutes – 50% fatal, 4-5 minutes – possible recovery. |
| 4-6% | Coma in 40 seconds Spermatic breathing and Death. |

Oxygen Enriched Atmospheres :
- Oxygen level above 23.5%.
- Causes flammable and combustible materials to burn violently when ignited.
- Hair, clothing, materials, etc.
- Oil-soaked clothing and materials.
- Never use pure oxygen to ventilate.
- Never store or place compressed tanks in a confined space.
Flammable Atmospheres :
- Two Critical Factors:
- Oxygen content in the air.
- Presence of flammable gas, or vapor like (Methane, hydrogen, Acetylene, Propane, Gasoline fumes, etc)
- Presence of dust (visibility of 5’ or less)
- Proper air/gas mixture can lead to an explosion
- Typical Ignition Sources:
- Sparking or electric tool.
- Welding/cutting operations.
- Smoking
Toxic Atmospheres :
- Product stored in a confined space:
- Gases released when cleaning. (Toxic materials are Carbon monoxide, Hydrogen Sulfide, welding fumes, corrosive, etc.)
- Materials absorbed into walls of confined space.
- Decomposition of materials in the confined space.
- Work performed in a confined space:
- Welding, cutting, brazing, soldering.
- Painting, scraping, sanding, degreasing.
- Sealing, bonding, melting.
- Areas are adjacent to a confined space.
Mechanical hazards
- Mixer
- Crushers
Effect of carbon monoxide:
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an Odorless, Colorless gas and Quickly collapses at high concentrations.
| PPM(CO Level) | EFFECT | TIME |
| 50 | Permissible Exposure Level | 8 Hours |
| 200 | Slight headache, discomfort | 3 Hours |
| 400 | Headache, discomfort | 1 Hours-2 Hour |
| 800 | Confusion, nausea, headache | 2 Hours |
| 1000 | Tendency to stagger | 1 1/5 Hours |
| 2000 | Slight heart palpitation | 30 Minute |
| 2000-3000 | Unconsciousness | Death in less than 30 Minute |
Confined space control measures:
The hierarchy of control measures to eliminate or minimize the risk should be followed in the priority order listed and consists of the following steps:
- Elimination
- Substitution
- Isolation
- Engineering controls
- Administrative controls
- Use of PPEs.
- Use of rescue tools.
Permit required for confined space:
- Contains or has the potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere.
- Contains a material that has the potential for engulfing an entrant.
- The internal configuration might cause an entrant to be trapped or asphyxiated by inwardly converging walls or floor that slopes downward and tapers to a smaller cross-section.
- Contains any other recognized serious safety or health hazard.
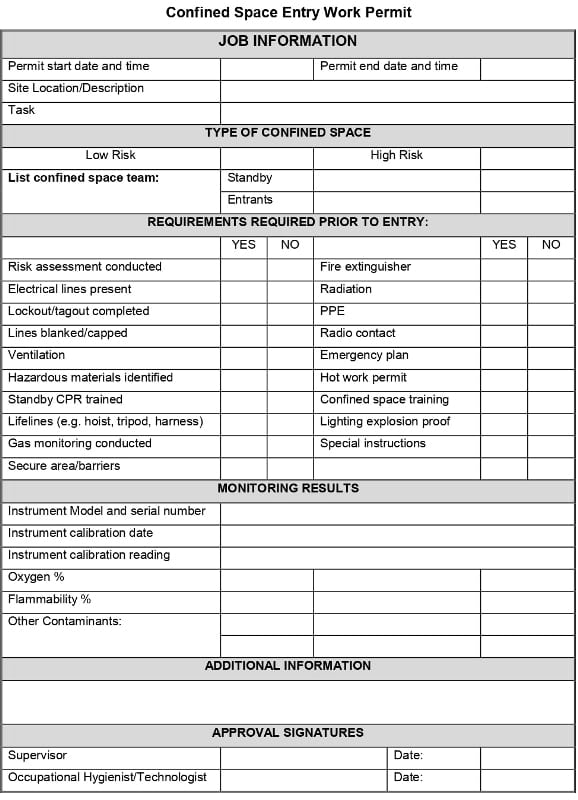
Contents of The Entry Permit:
- Permit space to be entered
- Purpose of the entry
- Date and the authorized duration of the entry permit
- Authorized entrants
- Attendants
- Site supervisor with a space for the signature
- Hazards of the permit space
- Measures used to isolate the permit space and to eliminate or control permit space hazards before entry
- Acceptable entry conditions
- Results of initial and periodic tests, names or initials of the testers and when the tests were performed
- Rescue and emergency services
- Communication procedures
- Equipment (personal protective equipment, testing equipment, communications equipment, alarm systems, rescue equipment, etc.)
- Any other information necessary in order to ensure employee safety
Confined space Work-permit
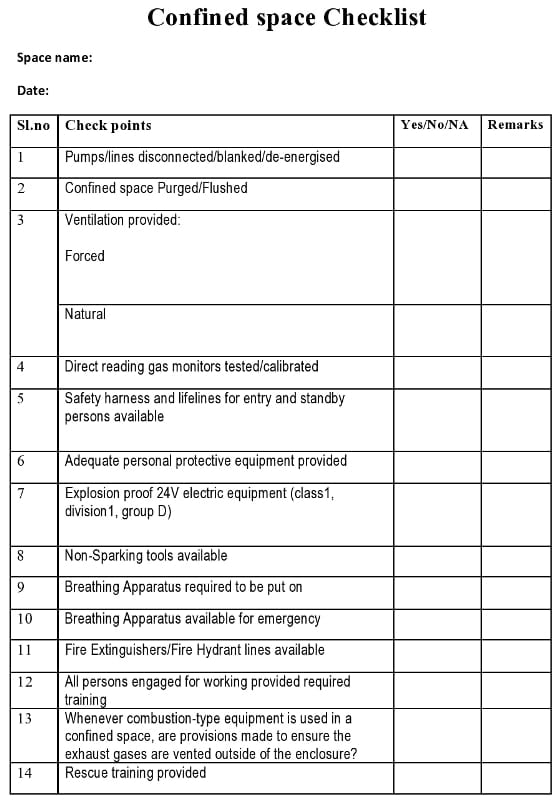
Confined space Checklist:
Confined space Requirements:
Precautions to be taken before entry to confined space:
- Ventilate, eliminate, or control the space’s atmospheric hazards.
- Blind or disconnect and cap all input lines so that no hazardous materials can enter the space.
- Lockout tag out (Positive Isolation).
- When entrance covers are removed, guard the opening immediately.
Atmospheric Monitoring:
- Test permit space before entry.
- Periodically monitor permit space to determine if entry conditions are maintained.
- Observe the status of existing hazards and those created during entry operations.
- Test all areas (top, middle, & bottom). Test atmosphere in this order:
- Check for Oxygen Content:
- At least 19.5% and less than 23.5% oxygen level required.
- Check for Combustibles:
- Less than 10% of the LEL
- Check for Toxic Gasses:
- Most commonly carbon monoxide (TLV <50 ppm)
- or any other hazardous materials as determined by the use of the space.
- Check for Oxygen Content:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE’s) requirement for confined space:
- Full-body Harness
- Respirator (half-mask, gas mask, Airline Respirator, etc.)
- Tyvek suit
- Helmet, safety shoe, safety goggles, nose mask, proper clothing, and suitable hand gloves.
Ventilation required for confined space:
- Use mechanical ventilation
- Fans
- Air horns
- Ventilate at the rate of at least four (4) volumes per hour
- Larger spaces require more ventilation.
- Make sure the air supply is not contaminated
- Ventilation air supply must be from fresh air uncontaminated with flammables, toxins, etc.
Confined space equipment list:
- Testing and monitoring equipment
- Ventilating equipment
- Communications equipment
- Lighting equipment
- Barriers
- Equipment needed for safe entry and exit
- Emergency equipment
- Other equipment for safe entry
- Rescue arrangements.
Rescue and Emergency Services for confined space
- Self-Rescue
- Non-entry Rescue
- Fire/Rescue – Call Fire Brigade
- The supervisor shall inform Emergency Control Agencies of the hazards they may encounter on site
- Provide the rescue provider with access to all permit spaces so they can develop rescue plans and practice rescue operations
Confined space rescue equipment list:
- Each entrant shall use a full-body harness (and a retrieval line if feasible).
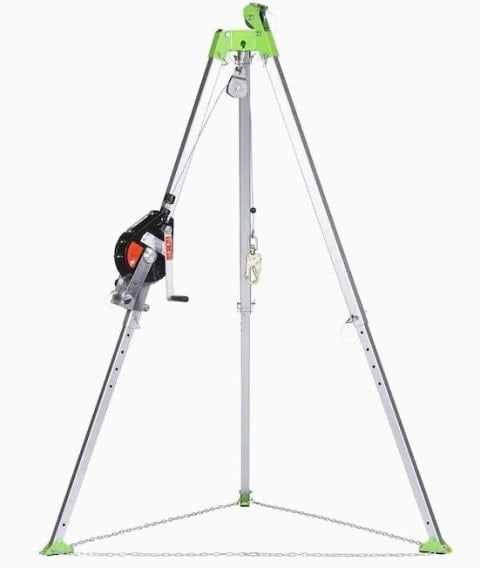
- A mechanical retrieval device (Tripod) shall be available for vertical type permit spaces.
- Retrieval systems shall be used unless they increase the overall risk of entry or would not contribute to the rescue.
- For Fire Call Fire Brigade.

Welding operation in confined space:
- Continuous ventilation should be provided in the confined space. Pure oxygen should never be used for ventilation.
- Conduct continuous monitoring throughout the entry to ensure that the area remains safe for entrants.
- Gas cylinders and welding power sources should remain outside the confined space.
Duties of Attendants in confined space:
- Communicate with entrants to monitor entrant status and to alert entrants if the need to evacuate arises.
- Monitor activities inside & outside the space and keep unauthorized individuals away.
- Summon Emergency Services.
- Perform non-entry rescues when applicable and they have training.
- Perform no duties that might interfere with the primary duty to monitor and protect entrants.
Vessel Entry Permit :
Tanks, vats, pits, sumps, vessels, floor opening, etc. should be protected by guard rails or cover. A fixed ladder with a handrail if possible should be provided to step down safely. A Portable (rope) ladder may be used while working inside a tank or vessel for temporary work. Precautions are:
- Check the concentration of toxic or flammable gas, dust, vapour etc., by a gas detector. Oxygen content should also be checked for safe proportion. It should be >18%.
- Airline or self-contained breathing apparatus and safety belt are essential.
- Sump pumps with flameproof electric or pneumatic motors and air extraction fans (spark-proof) and exhaust ducting to remove heavy vapors are necessary.
- Complete isolation of the vessel, cleaning, purging, and ventilation of the vessel, inspection and testing, safety permits, and all rescue arrangements must be done before such work and only a trained worker will work under constant help and supervision.
- The latest safety and rescue systems should be used. Winch arrangement connected with the worker’s harness is useful to lower and pull out quickly. Handfree communication system is available to keep the worker in the tank in constant touch with the supervisor outside. Hand-operated clutch, cord, and chair assembly can be used to lower the person while working at height or depth.
- The bottom drain valve and other nozzles should be kept open to allow good ventilation and fresh air in a vessel or tank.
Before allowing a vessel (confined space) entry permit, it is necessary to carry out a hazard assessment of the space. Therefore two types of formats are given below for use. Necessary changes as per specific requirements should be incorporated.
FAQs For Confined Space:
Here are some of the frequently asked questions and answers related to Confined Space.
What is the minimum oxygen level for a confined space?
The minimum safe level of oxygen in a confined space is 19.5%.
What is the maximum oxygen level for a confined space?
The maximum safe level of oxygen in a confined space is 23.5%.
what is the hazard of confined space?
1.Oxygen deficiency
2.Oxygen enriched
3.Combustible atmospheres
4.Toxic materials
5.Mechanical hazards
6.High temperature
What 3 things make a confined space?
1.Large enough to bodily enter and work.
2.Limited entry and exit.
3.Not designed for continuous human occupancy.
How long is a confined space permit valid for?
A permit is only valid for one shift.

