Basically, the safety color codes are identifying the type of hazards that are present in the workplace and that helps the workers to stay alert. So that it reduces accidents. Safety color code is most desirable and useful everywhere.
Table of Contents
Benefits of safety color code:
- Improve lighting conditions.
- Decorate the environment.
- Increase efficiency and productivity.
- Improve the quality of workmanship and normal skill.
- Improve labor morale and interest in work.
- Reduce accidents and increase safety.
- Reduce absenteeism.
- Raise the standard of good housekeeping.
- Improve building and machinery maintenance.
- Reduce hidden costs of dull and gloomy atmosphere, and
- Improve overall psychological and physiological effects on workers for better work performance.
Light-reflecting value:
LFV stands for light reflecting value. Pure white reflects 100% whereas pure black reflects 0% when light falls on them. The percentage of reflected light for other colors is given below.
| Colour | Percentage of reflected light in a light color | Percentage of reflected light in Medium color |
| Yellow | 75 | 65 |
| Grey | 75 | 55 |
| Green | 65 | 52 |
| Blue | 55 | 35 |
| Red | 40 | 20 |
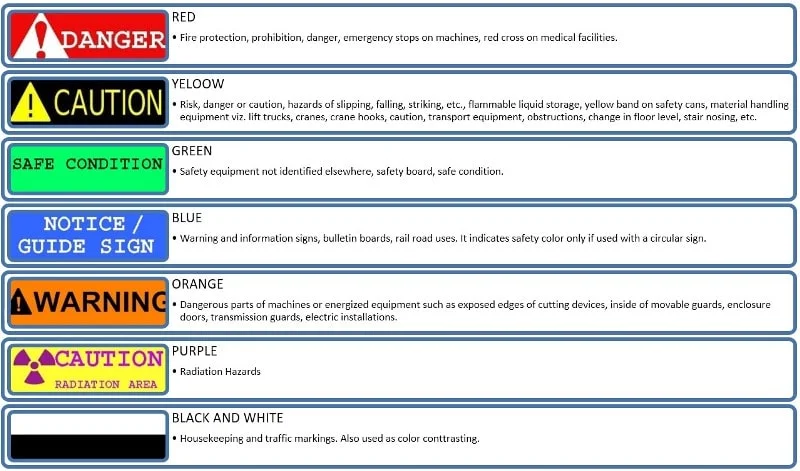
Colour coding to identify hazards:
Red – Fire protection, prohibition, danger, emergency stops on machines, red cross on medical facilities.

Yellow – Risk, danger or caution, hazards of slipping, falling, striking, etc., flammable liquid storage, yellow band on safety cans, material handling equipment viz. lift trucks, cranes, crane hooks, caution, transport equipment, obstructions, change in floor level, stair nosing, etc.

Green – Safety equipment not identified elsewhere, safety board, safe condition.
Blue – Warning and information signs, bulletin boards, railroad uses. It indicates a safety color only if used with a circular sign.
Orange – Dangerous parts of machines or energized equipment such as exposed edges of cutting devices, inside of movable guards, enclosure doors, transmission guards, electric installations.

Purple – Radiation Hazards.

Black & White – Housekeeping and traffic markings. Also used as contrast colors.
Pipeline color coding:
The pipelines in plants or industries carry harmless or hazardous contents. So it is most important to identify them. The proper color may be applied to the entire length of the pipe or in bands of 20-25 centimeters wide near the valves, pumps, and at repeated intervals along the line.
Anti-resistant colors should be used where acids and other chemicals may affect the paints. The entire length or a portion, more than 30 cm, of a pipeline should be painted so that it should not be mistaken for a color band. For longer pipes, the interval may be 50m.
| Material | colors |
| Water | Sea green |
| Steam | Aluminum |
| Air | Sky blue |
| Acid | Dark violet |
| Alkalis | Smoke grey |
| Minerals, vegetable oil, and animal oil | Light brown |
| Other gases or liquids do not need identification. | Black |
| Contents in the piping | Colour |
| Flammable or water for fire protection. | Red. |
| Dangerous (hazardous chemical) | Yellow. |
| Safe (water, air) | Green. |
| Protective material (inert gas) | Blue |
OSHA color codes:
Osha’s recommended color code is given below:
“DANGER” – Red, or predominantly red, with lettering or symbols in a contrasting color.
“CAUTION” – Yellow, or predominantly yellow, with lettering or symbols in a contrasting color.
“WARNING” – Orange, or predominantly orange, with lettering or symbols in a contrasting color.
“BIOLOGICAL HAZARD” – Fluorescent orange or orange-red, or predominantly so, with lettering or symbols in a contrasting color.
NOTE:
The information contained in this article is intended for general information purposes only and is based on information available as of the initial date of publication. No representation is made that the information or references are complete or remain current. This article is not a substitute for a review of current applicable government regulations, industry standards, or other standards specific to your business and/or activities and should not be construed as legal advice or opinion. Readers with specific questions should refer to the applicable standards or consult with an attorney.